Running Ansible Playbooks on Edge Devices
There may be cases in which you would like to be able to execute a scripts or commands in a device or on a group of devices. For example, in...
Read MorePublished on Apr 15, 2022 by Jakub Dżon on guide raspberry pi fedora flotta
Raspberry Pi is a very popular platform for running as an edge device in many, very different use cases like home automation, sensors deployment, vehicle deployment or many other cases.
Let’s learn how Flotta can be used to manage it by following steps described in this article.
1) Download Fedora IoT 36 Raw Image
2) Plug your SD card to your computer; in my case it will be available as /dev/sdb device:
$ lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINTS
sda 8:0 1 0B 0 disk
sdb 8:16 1 14.5G 0 disk
sdc 8:32 1 0B 0 disk
sdd 8:48 1 0B 0 disk
3) Make sure that you have arm-image-installer installed in your system.
In Fedora:
sudo dnf install arm-image-installer
4) Use arm-image-installer tool to burn downloaded Fedora image to the SD card:
sudo arm-image-installer --image=Fedora-IoT-35-20220101.0.aarch64.raw.xz --target=rpi4 --media=/dev/sdb --addkey=/home/jdzon/.ssh/id_rsa.pub --norootpass
Options used:
--image specifies which image file needs to be used for card preparation;--target specifies that the card is prepared for Raspberry Pi 4;--media specifies path to SD card device - will vary from system to system;--addkey will install given public key in the target system;--norootpass will allow root to login to the device without password.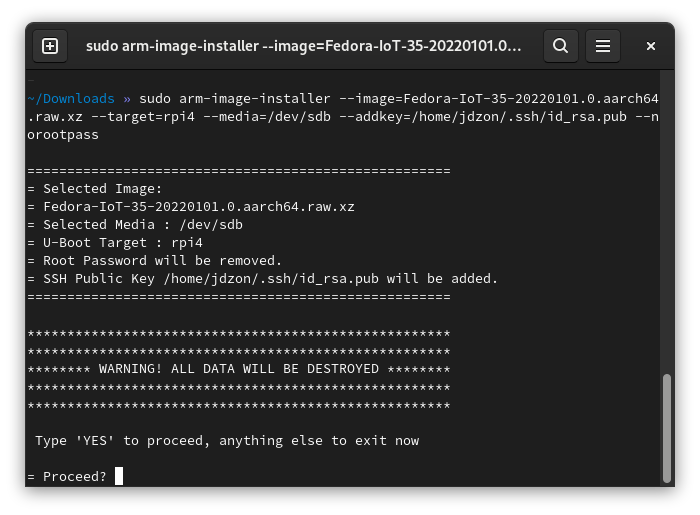
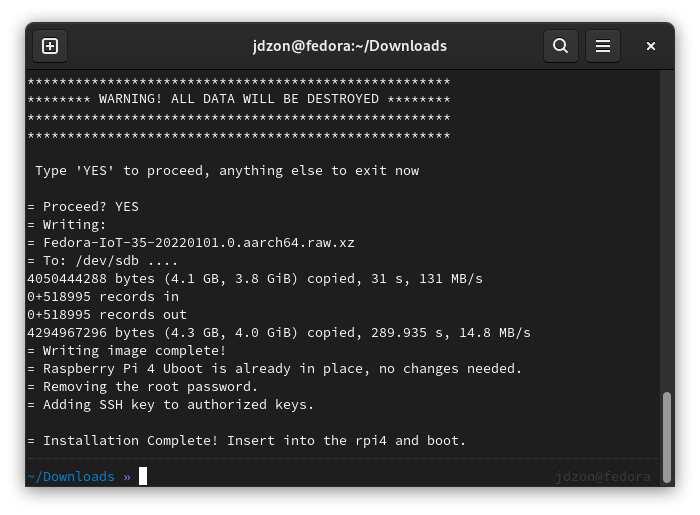
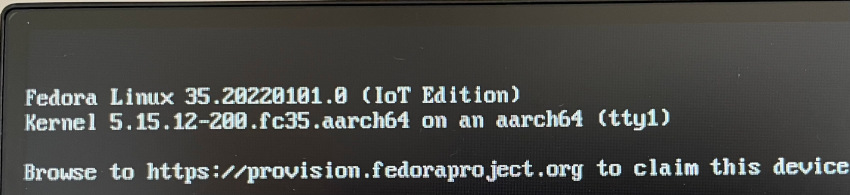
5) Plug freshly-prepared card into your Raspberry Pi and boot it.
Raspberry Pi running Fedora 35 IoT:

At the begining there are no edge devices registered with our cluster:
$ watch -t kubectl get edgedevice
No resources found in default namespace.
Brand new Raspberry Pi does not have Flotta agent configured (in this case, the service is called yggdrasild):
$ systemctl status yggdrasild
Unit yggdrasild.service could not be found.
On the machine with $KUBECONFIG pointing to our cluster with Flotta Operator installed execute following command in the
flotta-operator repository to create dedicated agent bootstrap script:
$ make agent-install-scripts
As a result hack/install-agent-rpm-ostree.sh script is generated, and it needs to be transferred to our Raspberry Pi device.
$ sftp root@10.220.200.110 1 ↵ jdzon@fedora
Connected to 10.220.200.110.
sftp> put hack/install-agent-rpm-ostree.sh
Uploading hack/install-agent-rpm-ostree.sh to /var/roothome/install-agent-rpm-ostree.sh
install-agent-rpm.sh
$
On the computer with $KUBECONFIG pointing to our cluster, let’s forward required port to make HTTPS API public:
For Flotta Operator version > v0.1.0:
$ kubectl port-forward service/flotta-edge-api -n flotta 8043 --address 0.0.0.0
Forwarding from 0.0.0.0:8043 -> 8043
For Flotta Operator version v0.1.0:
$ kubectl port-forward service/flotta-operator-controller-manager -n flotta 8043 --address 0.0.0.0
Forwarding from 0.0.0.0:8043 -> 8043
IP address of the machine exposing the API is 10.220.200.106.
On the device, let’s execute the uploaded script, providing IP address of machine making Flotta Operator HTTP API public.
At the end of its execution, the script will restart the Raspberry Pi device; it may take a while for the device to be available again.
./install-agent-rpm-ostree.sh -i 10.220.200.106
Let’s monitor EdgeDevice object in our cluster to see when the device becomes available:
$ watch -t kubectl get edgedevice
NAME AGE
171303c8224e4b27a0f4dbb4a351e397 5s
The yggdrasild service is running on the device:
$ systemctl is-active yggdrasild
active
Let’s make some use of our Flotta-configured device - let’s deploy an HTTP server there - we will use Nginx for arm64
container image in our EdgeWorkload.
To pick device to run our workload, we need to specify labels the device must have to run our Nginx server. Because we
use arm64 version of Nginx, let’s use a label that shows that; the EdgeDevice CR already has device.cpu-architecture
label assigned thanks to Flotta agent hardware discovery:
$ kubectl get edgedevice 171303c8224e4b27a0f4dbb4a351e397 -ojsonpath="{.metadata.labels}"
{"device.cpu-architecture":"aarch64","device.cpu-model":"cortex-a72","device.hostname":"fedora","device.system-manufacturer":"unknown","device.system-product":"unknownproduct","device.system-serial":"10000000935120b5"}
To be more picky about the devices we want to use, let’s create custom profile=http label to show that the device is an HTTP server. Let’s add it:
kubectl label edgedevice 171303c8224e4b27a0f4dbb4a351e397 profile=http
After all that preparation, we can create our Nginx arm64 EdgeWorkload:
kubectl apply -f -<<EOF
apiVersion: management.project-flotta.io/v1alpha1
kind: EdgeWorkload
metadata:
name: http-nginx
spec:
deviceSelector:
matchLabels:
profile: http
device.cpu-architecture: aarch64
type: pod
pod:
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: quay.io/jdzon/nginx-rpi:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 80
hostPort: 9090
EOF
and monitor for the workload to be running:
$ watch -t kubectl get edgedevice 171303c8224e4b27a0f4dbb4a351e397 -ojsonpath="{.status.workloads}"
At first it will be just:
[{"name":"http-nginx","phase":"Deploying"}]
but after a while it would show that our nginx server is running:
[{"lastTransitionTime":"2022-04-15T13:38:37Z","name":"http-nginx","phase":"Running"}]
The device should show our nginx pod running:
$ podman pod ps
POD ID NAME STATUS CREATED INFRA ID # OF CONTAINERS
5837e232f808 http-nginx Running 2 minutes ago 69c7dc07a3f3 2
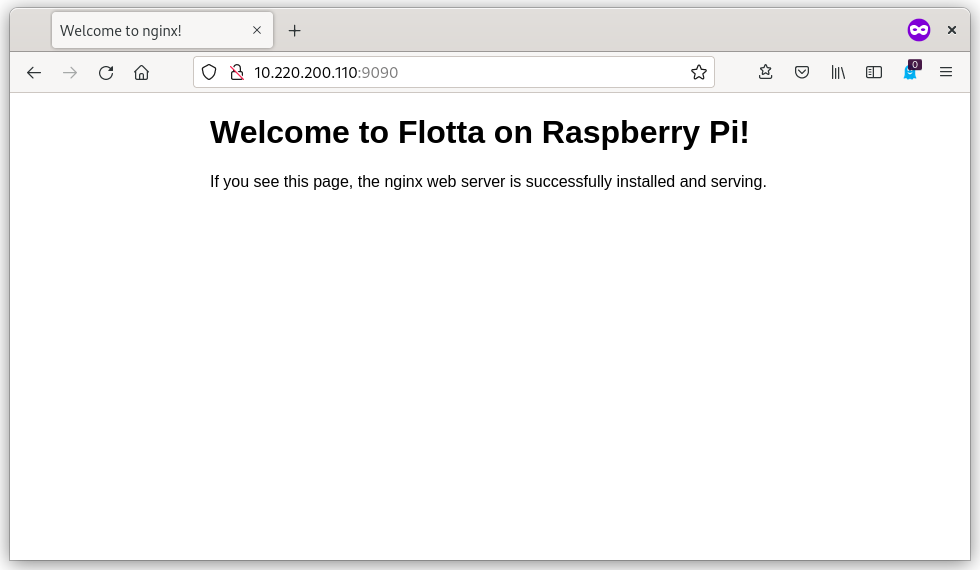
The device should have our Nginx server available under port 9090 - let’s check if it’s working:
$ curl 10.220.200.110:9090
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Welcome to nginx!</title>
<style>
html { color-scheme: light dark; }
body { width: 35em; margin: 0 auto;
font-family: Tahoma, Verdana, Arial, sans-serif; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to Flotta on Raspberry Pi!</h1>
<p>If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed and
serving.</p>
</body>
</html>
Having read the above description you should be well-equipped to use Flotta to run your aarch64 workloads on your own Raspberry Pi ran under Fedora IoT supervision.
Thank you for reading!
There may be cases in which you would like to be able to execute a scripts or commands in a device or on a group of devices. For example, in...
Read MoreEdge Example App is an app for Flotta Edge devices, with a workload that will be deployed on the device that has two main features: Sensing the Internet (which helps...
Read MoreEdge Example App is an app for Flotta Edge devices, with a workload that will be deployed on the device that has two main features:
Read More